The RabbitMQ routing pattern is basically the same as the publish/subscribe pattern, with the difference being that the publish/subscribe pattern forwards messages to all bound queues, while the routing pattern forwards messages to the queue based on the routing match.
From a specific coding perspective, the difference between the routing pattern and the publish/subscribe pattern lies in the type of exchange used. The routing pattern uses the Direct type.
Architecture Diagram
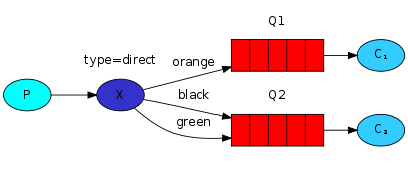
Explanation:
- P represents the producer, C1 and C2 represent the consumers, the red boxes represent queues, and X represents the exchange.
- Exchange type is direct.
- Direct exchange message forwarding logic: compare the Routing key in the message with the Routing keys associated with all Bindings of this Exchange. If they are equal, the message is sent to the Queue corresponding to that Binding.
For example, in the above diagram: The routing key for queue Q1 is orange, and the routing keys for queue Q2 are black and green. When sending a message, if the message's routing key is orange, it will be forwarded to queue Q1, and if the message's routing key is black or green, it will be forwarded to queue Q2.
Use Cases
The routing pattern is an extension of the publish/subscribe pattern, so the use cases are similar to the publish/subscribe pattern, with the difference being the ability to set message subscription conditions.
For example: In an e-commerce website, there are four warehouses in East China, South China, North China, and Southwest China, each of which has a set of warehouse management systems deployed. When a user makes a purchase order, the nearest warehouse is responsible for shipping.
After a user places an order and a purchase order message is generated, we want to forward the message to the corresponding regional warehouse management system for processing, which can be achieved using the routing pattern.
The routing key bindings for the delivery queues of the four warehouse management systems are as follows:
- East China = east
- North China = north
- South China = south
- Southwest China = west
After a user places an order, determine which region the user's address belongs to, calculate the routing key, and then send the order message with the routing key. The RabbitMQ direct exchange will forward it to the corresponding queue.