The Golang RabbitMQ topic mode is similar to the routing mode (Direct), with the biggest difference being that the routing parameters in the topic mode support fuzzy matching. The exchange type for the topic mode is ‘topic’.
The architecture of the topic mode is as follows: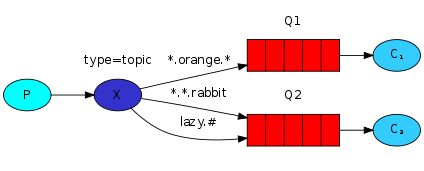
Note: If you are not familiar with the RabbitMQ topic mode, please read the RabbitMQ topic mode section first.
1. Prerequisite Tutorial
Please read the following sections in order:
- RabbitMQ basic concepts section
- RabbitMQ topic mode section
- Implementing Golang RabbitMQ publish/subscribe pattern section
Note: Because the Golang RabbitMQ publish/subscribe section already contains complete code examples, only the exchange definition and routing parameters are different for other RabbitMQ modes. Therefore, only the key code is shown.
2. Declaring Topic Exchange
err = ch.ExchangeDeclare(
"tizi365_topic", // Exchange name, needs to be unique
"topic", // Exchange type
true, // Durable
false, // Auto-deleted
false, // Internal
false, // No-wait
nil, // Arguments
)
3. Sending Messages
// Message content
body := "Hello Tizi365.com!"
// Publish message
err = ch.Publish(
"tizi365_topic", // Exchange name
"www.tizi365.com", // Routing parameter, crucial parameter determining which queue your message will be sent to
false, // Mandatory
false, // Immediate
amqp.Publishing {
ContentType: "text/plain", // Message content type, here it is plain text
Body: []byte(body), // Message content
})
4. Consuming Messages
4.1. Binding Exchange
// Declare the queue to be operated on
q, err := ch.QueueDeclare(
"", // Queue name, will be generated randomly if not filled
false, // Durable queue
false, // Delete when unused
true, // Exclusive
false, // No-wait
nil, // Arguments
)
// Bind the queue to the specified exchange
err = ch.QueueBind(
q.Name, // Queue name
"*.tizi365.com", // Routing parameter, crucial parameter, using the wildcard * to match one word, if # is used, it can match multiple words
"tizi365_topic", // Exchange name, needs to match the exchange defined by the message sender
false,
nil)
4.2. Handling Messages
// Create a consumer
msgs, err := ch.Consume(
q.Name, // Reference to the queue name above
"", // Consumer name, automatically generated if not filled
true, // Automatic acknowledgment to the queue that the message has been handled
false, // Exclusive
false, // No-local
false, // No-wait
nil, // Args
)
// Iterate through consuming messages in the queue
for d := range msgs {
log.Printf("Received message=%s", d.Body)
}