Simple Queue Mode of Golang RabbitMQ
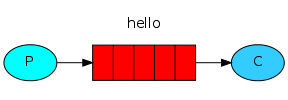
Explanation:
P represents the producer, C represents the consumer, and red represents the queue.
Note: If you are not familiar with RabbitMQ, please read the RabbitMQ Basic Concepts section first.
1. Install Dependencies
go get github.com/streadway/amqp
Import the dependency package
import (
"github.com/streadway/amqp"
)
2. Send Messages
The following steps demonstrate how the message producer completes the message push.
2.1. Connect to RabbitMQ Server
// Connect to RabbitMQ Server
conn, err := amqp.Dial("amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/")
defer conn.Close()
Connection address explanation:
amqp://username:password@RabbitMQAddress:port/
2.2. Create a Channel
Most operations are performed on the channel.
ch, err := conn.Channel()
defer ch.Close()
2.3. Declare a Queue
Represents the queue we need to read or write from.
q, err := ch.QueueDeclare(
"hello", // Queue name
false, // Message persistence
false, // Delete the queue when not in use
false, // Exclusive
false, // No-wait
nil, // Arguments
)
2.4. Push Messages
// Message content
body := "Hello World!"
// Push the message
err = ch.Publish(
"", // Exchange (ignore here)
q.Name, // Routing parameter, use the queue name as the routing parameter
false, // Mandatory
false, // Immediate
amqp.Publishing {
ContentType: "text/plain",
Body: []byte(body), // Message content
})
2.5. Complete Code for Sending Messages
package main
// Import packages
import (
"log"
"github.com/streadway/amqp"
)
// Handle errors
func failOnError(err error, msg string) {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("%s: %s", msg, err)
}
}
func main() {
// Connect to RabbitMQ
conn, err := amqp.Dial("amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/")
failOnError(err, "Failed to connect to RabbitMQ")
defer conn.Close()
// Create a channel
ch, err := conn.Channel()
failOnError(err, "Failed to open a channel")
defer ch.Close()
// Declare the queue to operate
q, err := ch.QueueDeclare(
"hello", // Name
false, // Durable
false, // Delete when unused
false, // Exclusive
false, // No-wait
nil, // Arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare a queue")
// Message content to send
body := "Hello World!"
// Send the message
err = ch.Publish(
"", // Exchange
q.Name, // Routing key
false, // Mandatory
false, // Immediate
amqp.Publishing{
ContentType: "text/plain",
Body: []byte(body),
})
failOnError(err, "Failed to publish a message")
log.Printf(" [x] Sent %s", body)
}
3. Receiving Messages
The first three steps of receiving messages are the same as sending messages, corresponding to sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 respectively.
The complete code for receiving messages is as follows:
package main
// Import packages
import (
"log"
"github.com/streadway/amqp"
)
// Error handling
func failOnError(err error, msg string) {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("%s: %s", msg, err)
}
}
func main() {
// Connect to RabbitMQ
conn, err := amqp.Dial("amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/")
failOnError(err, "Failed to connect to RabbitMQ")
defer conn.Close()
// Create a channel
ch, err := conn.Channel()
failOnError(err, "Failed to open a channel")
defer ch.Close()
// Declare the queue to be operated on
q, err := ch.QueueDeclare(
"hello", // The queue name needs to be consistent with the queue name for sending messages
false, // durable
false, // delete when unused
false, // exclusive
false, // no-wait
nil, // arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare a queue")
// Create a message consumer
msgs, err := ch.Consume(
q.Name, // Queue name
"", // Consumer name, if not filled in, a unique ID will be generated automatically
true, // Whether to automatically acknowledge messages, i.e., automatically inform RabbitMQ that the message has been successfully processed
false, // exclusive
false, // no-local
false, // no-wait
nil, // args
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to register a consumer")
// Fetch messages from the queue in a loop
for d := range msgs {
// Print message content
log.Printf("Received a message: %s", d.Body)
}
}