Worksheet
Set Column Visibility
func (f *File) SetColVisible(sheet, col string, visible bool) error
Set the visibility of the given column based on the specified worksheet name and column name. This function is concurrency-safe. For example, to hide column D on the worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.SetColVisible("Sheet1", "D", false)
Hide columns D to F on the worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.SetColVisible("Sheet1", "D:F", false)
Set Column Width
func (f *File) SetColWidth(sheet, startCol, endCol string, width float64) error
Set the width of one or more columns based on the given worksheet name, column range, and width value. This function is concurrency-safe. For example, to set the width of columns A to H on the worksheet named Sheet1 to 20:
err := f.SetColWidth("Sheet1", "A", "H", 20)
Set Row Height
func (f *File) SetRowHeight(sheet string, row int, height float64) error
Set the height of a single row based on the given worksheet name, row number, and height value. For example, to set the height of the first row on the worksheet named Sheet1 to 50:
err := f.SetRowHeight("Sheet1", 1, 50)
Set Row Visibility
func (f *File) SetRowVisible(sheet string, row int, visible bool) error
Set the visibility of the specified row based on the given worksheet name and row number. For example, to hide the second row on the worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.SetRowVisible("Sheet1", 2, false)
Get Worksheet Name
func (f *File) GetSheetName(index int) string
Get the worksheet name based on the given worksheet index. If the worksheet does not exist, an empty string will be returned.
Get Column Visibility
func (f *File) GetColVisible(sheet, column string) (bool, error)
Get the visibility of the specified column in the worksheet based on the given worksheet name and column name. A return value of true indicates visibility, while false indicates invisibility. This function is concurrency-safe. For example, to get the visibility of column D on the worksheet named Sheet1:
visible, err := f.GetColVisible("Sheet1", "D")
Get Column Width
func (f *File) GetColWidth(sheet, col string) (float64, error)
Get the width of the specified column in the worksheet based on the given worksheet name and column name. This function is concurrency-safe.
Get Row Height
func (f *File) GetRowHeight(sheet string, row int) (float64, error)
Get the height of the specified row in the worksheet based on the given worksheet name and row number. For example, to get the height of the first row on the worksheet named Sheet1:
height, err := f.GetRowHeight("Sheet1", 1)
Get Row Visibility
func (f *File) GetRowVisible(sheet string, row int) (bool, error)
Get the visibility of the specified row in the worksheet based on the given worksheet name and row number. For example, to get the visibility of the second row on the worksheet named Sheet1:
visible, err := f.GetRowVisible("Sheet1", 2)
Get the index of a worksheet
func (f *File) GetSheetIndex(sheet string) (int, error)
Get the index of the given worksheet by its name. Return -1 if the worksheet does not exist. The obtained index can be used as the parameter when calling SetActiveSheet() function to set the default worksheet of the workbook.
Get the mapping of worksheets
func (f *File) GetSheetMap() map[int]string
Get the mapping of all worksheets, chart sheets, and dialog sheets in the workbook, represented by ID and name.
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("Book1.xlsx")
if err != nil {
return
}
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
for index, name := range f.GetSheetMap() {
fmt.Println(index, name)
}
Get the list of worksheets
func (f *File) GetSheetList() []string
Get the list of worksheets, including worksheets, chart sheets, and dialog sheets in the same order as they appear in the workbook.
Set the name of a worksheet
func (f *File) SetSheetName(source, target string) error
Rename the worksheet based on the given old and new worksheet names. The worksheet name can use up to 31 characters. This function only changes the name of the worksheet and will not update the formulas associated with cells or worksheet names in references. Therefore, using this function to rename a worksheet may result in formula errors or reference issues.
Insert columns
func (f *File) InsertCols(sheet, col string, n int) error
Insert empty columns before the specified column based on the given worksheet name, column name, and the number of columns to be inserted. For example, insert 2 empty columns before column C in the worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.InsertCols("Sheet1", "C", 2)
Insert rows
func (f *File) InsertRows(sheet string, row, n int) error
Insert empty rows before the specified row based on the given worksheet name, row number, and the number of rows to be inserted. For example, insert 2 empty rows before the 3rd row in the worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.InsertRows("Sheet1", 3, 2)
Append and copy rows
func (f *File) DuplicateRow(sheet string, row int) error
Append a duplicate after the given row number based on the given worksheet name. For example, duplicate the 2nd row of the worksheet named Sheet1 to the 3rd row:
err := f.DuplicateRow("Sheet1", 2)
Exercise caution when using this method, as it will affect all changes to the original formulas, charts, and other resource references in the worksheet. If the worksheet contains any reference values, opening it using an Excel application after using this method may lead to file errors. excelize currently only supports updates on partial references on the worksheet.
Duplicate Row
func (f *File) DuplicateRowTo(sheet string, row, row2 int) error
Duplicate the row after the specified row based on the given sheet name and row number. For example, duplicate the second row of the worksheet named Sheet1 after the seventh row:
err := f.DuplicateRowTo("Sheet1", 2, 7)
Please use this method with caution, as it will affect all changes in the original formulas, charts, and other resources referenced in the worksheet. If the worksheet contains any referenced values, opening it with an Excel application after using this method may result in file errors. excelize currently only supports updates to partially referenced on the worksheet.
Set Row Outline Level
func (f *File) SetRowOutlineLevel(sheet string, row int, level uint8) error
Create a group based on the given sheet name, row number, and outline level parameter. For example, create a level 1 group at the second row of the worksheet named Sheet1.
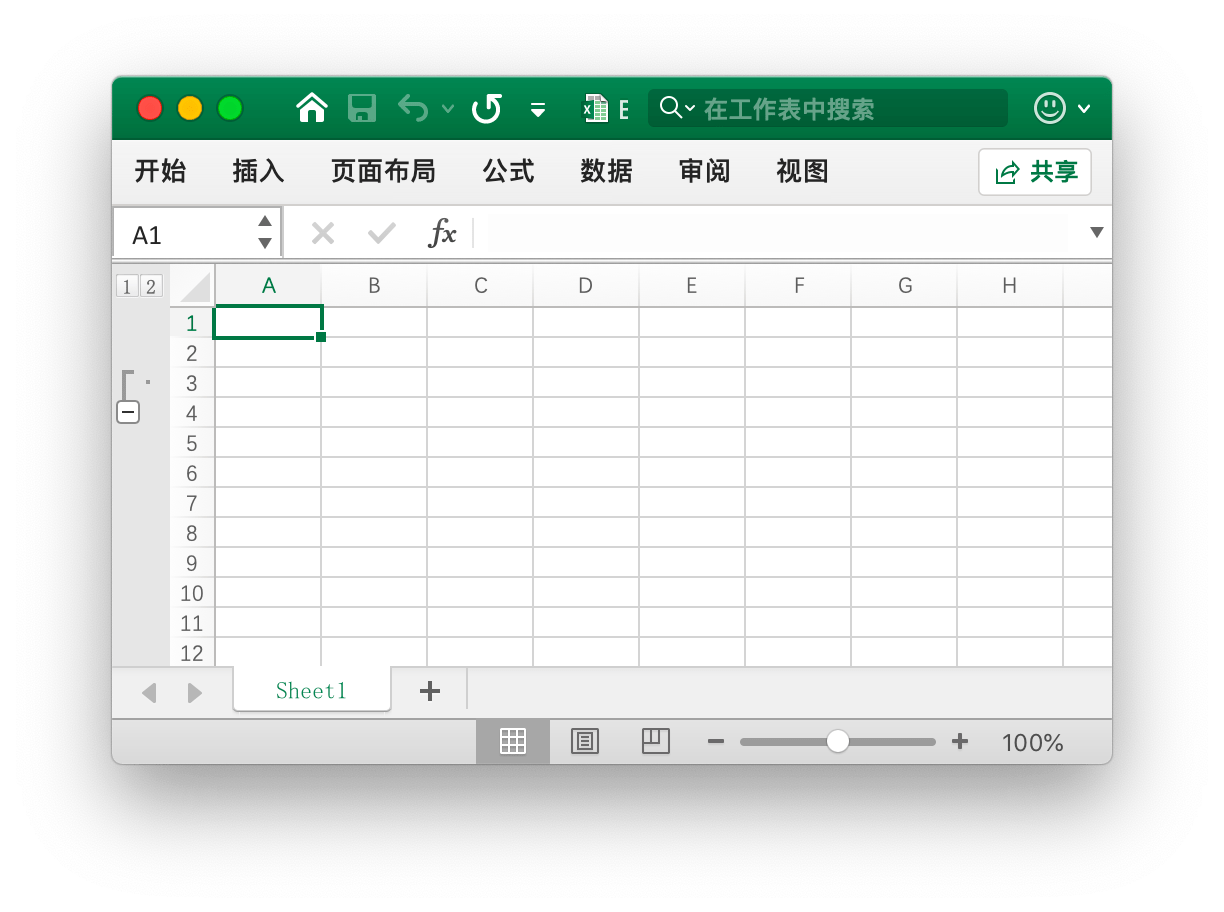
err := f.SetRowOutlineLevel("Sheet1", 2, 1)
Set Column Outline Level
func (f *File) SetColOutlineLevel(sheet, col string, level uint8) error
Create a group based on the given sheet name, column name, and outline level parameter. For example, create a level 2 group in the D column of the worksheet named Sheet1.
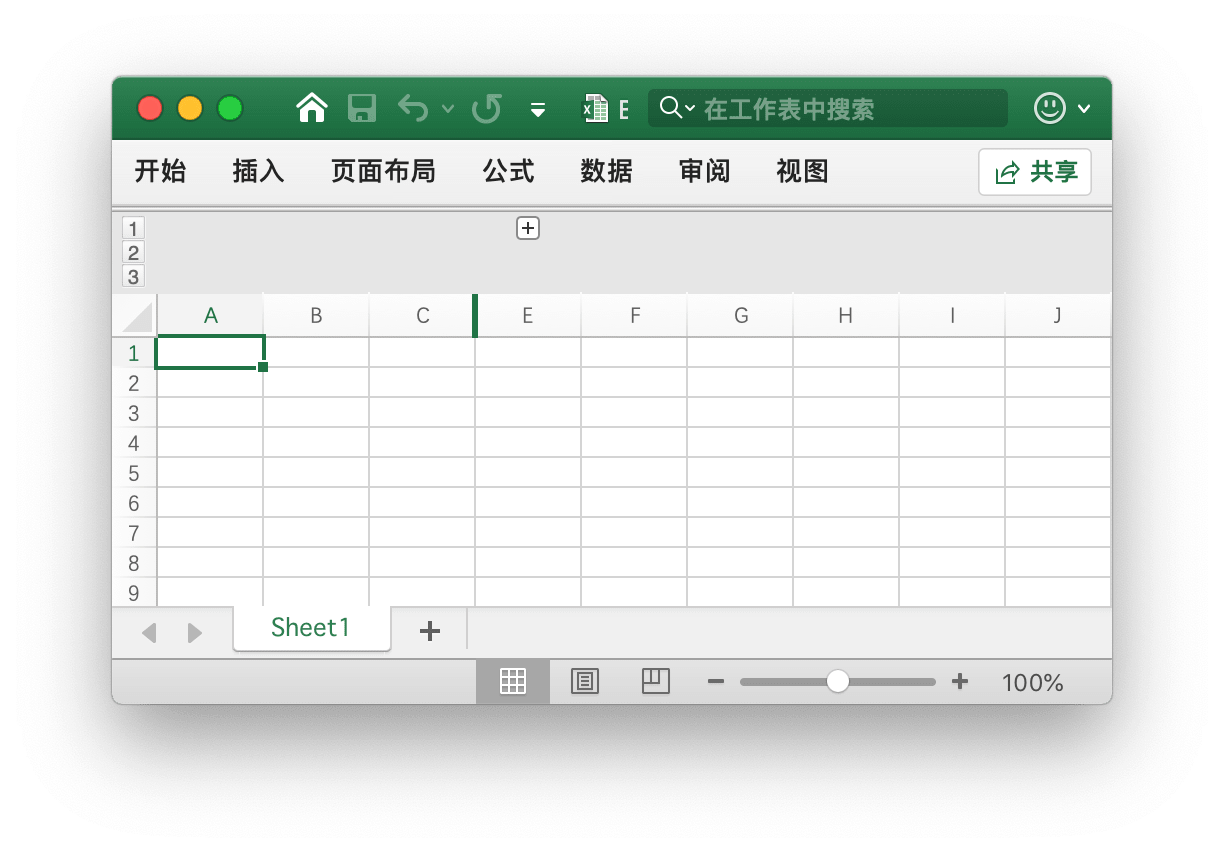
err := f.SetColOutlineLevel("Sheet1", "D", 2)
Get Row Outline Level
func (f *File) GetRowOutlineLevel(sheet string, row int) (uint8, error)
Get the outline level based on the given sheet name and row number. For example, get the outline level of the second row in the worksheet named Sheet1.
level, err := f.GetRowOutlineLevel("Sheet1", 2)
Get Column Outline Level
func (f *File) GetColOutlineLevel(sheet, col string) (uint8, error)
Get the outline level based on the given sheet name and column name. For example, get the outline level of the D column in the worksheet named Sheet1.
level, err := f.GetColOutlineLevel("Sheet1", "D")
Column Iterator
func (f *File) Cols(sheet string) (*Cols, error)
Get the column iterator of the specified worksheet based on the given sheet name. This function is concurrency safe. Use the column iterator for streaming read and cell traversal:
cols, err := f.Cols("Sheet1")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
for cols.Next() {
col, err := cols.Rows()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
for _, rowCell := range col {
fmt.Print(rowCell, "\t")
}
fmt.Println()
}
Column Iterator - Get Values of Single Column
func (cols *Cols) Rows(opts ...Options) ([]string, error)
Return the values of all rows in the current column.
Column Iterator - Traversal Operation
func (cols *Cols) Next() bool
Return true if there are values in the next column.
Column Iterator - Error Handling
func (cols *Cols) Error() error
Return an error when an error occurs while looking for the next column.
Row Iterator
func (f *File) Rows(sheet string) (*Rows, error)
Get the row iterator of the given sheet name. This function is concurrency-safe. Use the row iterator to iterate through cells for streaming read:
rows, err := f.Rows("Sheet1")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
for rows.Next() {
row, err := rows.Columns()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
for _, colCell := range row {
fmt.Print(colCell, "\t")
}
fmt.Println()
}
if err = rows.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
Row Iterator - Single Row Operation
func (rows *Rows) Columns(opts ...Options) ([]string, error)
This function streams reads the worksheet row by row, returning the values of each cell in the current row, without skipping valid blank rows at the end of the worksheet.
Row Iterator - Traversal Operation
func (rows *Rows) Next() bool
Returns true if there is a value in the next row.
Row Iterator - Error Handling
func (rows *Rows) Error() error
Returns an error when an error occurs during the search for the next row.
Row Iterator - Read Row Properties
func (rows *Rows) GetRowOpts() RowOpts
Returns the current row’s properties such as row height, visibility, and style ID.
Row Iterator - Close Data Stream
func (rows *Rows) Close() error
Closes the data stream and cleans up any system disk cache that may have been generated when opening the worksheet.
Search in Worksheet
func (f *File) SearchSheet(sheet, value string, reg ...bool) ([]string, error)
Get coordinates based on the given worksheet name, cell value, or regular expression. This function only supports full matches of strings and numbers, does not support calculated results, formatted numbers, and conditional searches. If the search result is a merged cell, the coordinates of the top-left corner of the merged area will be returned.
For example, search for the coordinates of the value 100 in the worksheet named Sheet1:
result, err := f.SearchSheet("Sheet1", "100")
For example, search for the coordinates of numeric values in the range 0-9 in the worksheet named Sheet1:
result, err := f.SearchSheet("Sheet1", "[0-9]", true)
Protect Worksheet
func (f *File) ProtectSheet(sheet string, opts *SheetProtectionOptions) error
Prevent other users from accidentally or intentionally changing, moving, or deleting data in the worksheet. The optional field AlgorithmName supports specifying the hash algorithm XOR, MD4, MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-384, or SHA-512. If the hash algorithm is not specified, the XOR algorithm will be used by default. For example, setting a password protection for the worksheet named Sheet1 but allowing locked cell selection, unlocked cell selection, and editing scenarios:
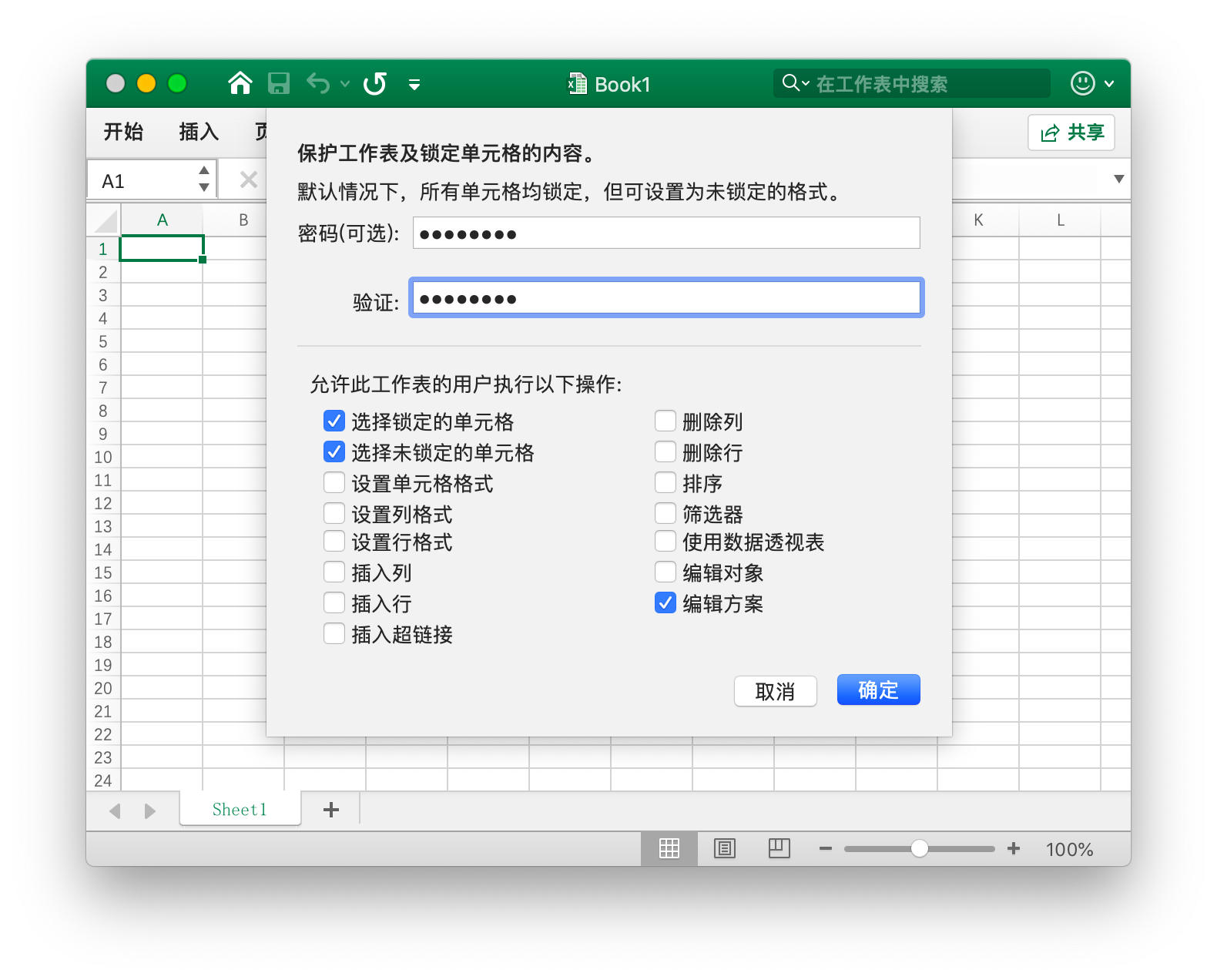
err := f.ProtectSheet("Sheet1", &excelize.SheetProtectionOptions{
AlgorithmName: "SHA-512",
Password: "password",
SelectLockedCells: true,
SelectUnlockedCells: true,
EditScenarios: true,
})
SheetProtectionOptions defines the settings options for protecting the worksheet.
type SheetProtectionOptions struct {
AlgorithmName string
AutoFilter bool
DeleteColumns bool
DeleteRows bool
EditObjects bool
EditScenarios bool
FormatCells bool
FormatColumns bool
FormatRows bool
InsertColumns bool
InsertHyperlinks bool
InsertRows bool
Password string
PivotTables bool
SelectLockedCells bool
SelectUnlockedCells bool
Sort bool
}
Unprotect Worksheet
func (f *File) UnprotectSheet(sheet string, password ...string) error
Unprotect the worksheet according to the given worksheet name, and specify the second optional password parameter to cancel the worksheet protection by password validation.
Remove Column
func (f *File) RemoveCol(sheet, col string) error
Delete the specified column according to the given worksheet name and column name. For example, delete the C column in the worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.RemoveCol("Sheet1", "C")
Please use this method with caution, as this will affect all changes to the original formula, chart, and other resource references in the worksheet. If the worksheet contains any referenced values, using this method may cause file errors when opened with Excel application after use. Excelize currently only supports partial updates on referenced values in the worksheet.
Remove Row
func (f *File) RemoveRow(sheet string, row int) error
Delete the specified row according to the given worksheet name and row number. For example, delete the 3rd row in the worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.RemoveRow("Sheet1", 3)
Please use this method with caution, as this will affect all changes to the original formula, chart, and other resource references in the worksheet. If the worksheet contains any referenced values, using this method may cause file errors when opened with Excel application after use. Excelize currently only supports partial updates on referenced values in the worksheet.
Assign Values by Column
func (f *File) SetSheetCol(sheet, cell string, slice interface{}) error
Assign values by column according to the given worksheet name, starting coordinates, and the reference of type slice. For example, assign values by column on column B of the worksheet named Sheet1, with cell B6 as the starting coordinate:
err := f.SetSheetCol("Sheet1", "B6", &[]interface{}{"1", nil, 2})
Assign by Row
func (f *File) SetSheetRow(sheet, cell string, slice interface{}) error
Assigns values by row based on the given worksheet name, starting coordinates, and the reference to the type of slice. This function is concurrency-safe. For example, on the 6th row of the worksheet named Sheet1, values can be assigned by row starting from cell B6:
err := f.SetSheetRow("Sheet1", "B6", &[]interface{}{"1", nil, 2})
Insert Page Break
func (f *File) InsertPageBreak(sheet, cell string) error
Inserts a page break based on the given worksheet name and cell coordinates. Page breaks are the dividing lines that separate the worksheet into individual pages for printing purposes.
Remove Page Break
func (f *File) RemovePageBreak(sheet, cell string) error
Removes a page break based on the given worksheet name and cell coordinates.
Set Worksheet Dimension
func (f *File) SetSheetDimension(sheet string, rangeRef string) error
Sets or removes the used area of the worksheet based on the given worksheet name and cell coordinates or cell coordinate range. The used cells include cells with formulas, text content, and cell formatting, for example, A1:D5. When the given cell coordinate range is an empty string, it will remove the used area of the worksheet.
Get Worksheet Dimension
func (f *File) GetSheetDimension(sheet string) (string, error)
Obtains the used area of the specified worksheet based on the given worksheet name.